Because Arabic is such a large language. It is a veritable treasure trove of various dialects. These dialects differ from one another, but some are also very similar. A comparison between Arabic dialects can clear the picture vividly.
This is due to the physical distance between them. For example, if one dialect is close to another, they are similar. The closer dialects exist to each other, the more similar they are, and the farther dialects exist from each other, the more different they are.
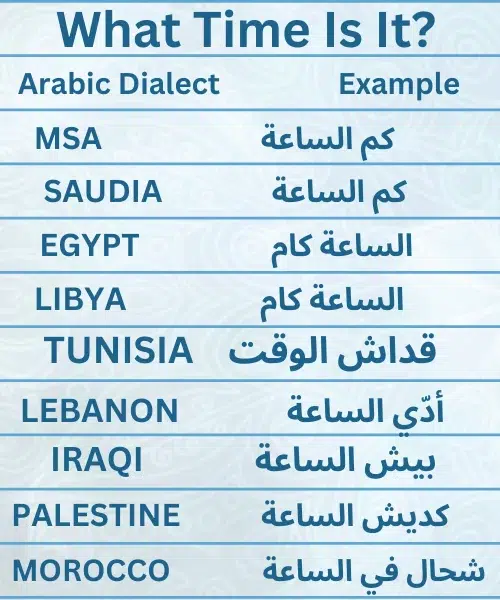
These dialects are also distinct from one another because each dialect is influence by nearby other languages. Each dialect gains new and modified words in this manner.
All of these dialects are more or less similar, but they are all mutually intelligible. Some are more understandable than others.

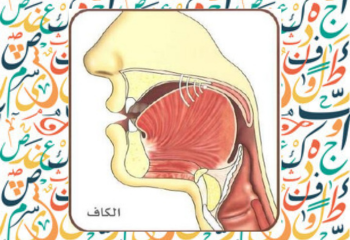
In the Egyptian dialect, the sound ” g ” is replace with ” j “.
There are two major varieties of Iraqi dialects: Gelet and Qeltu. The former is a more formal way of saying “I said,” whereas the latter sounds like it was spoken locally! The “q” sound can be replace with a “g” depending on the region, a feature shared by Gulf dialects.
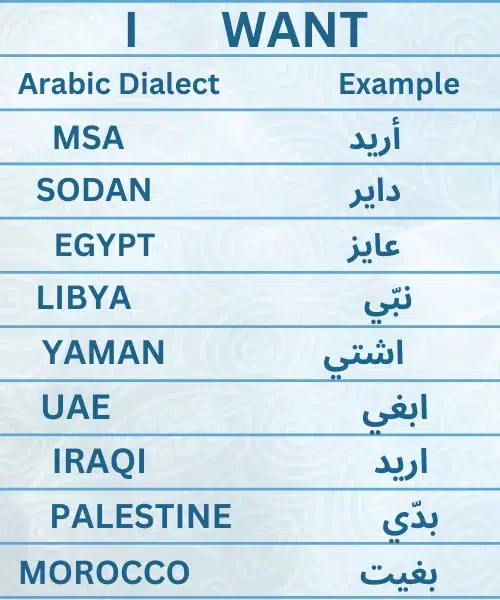
The th-sound is usually replace with an “s” or “z” in the Levantine dialect, but accent-level differences are common throughout the region. The “Qaf” sound is not pronounce in Levantine Arabic and is replace with a “Alif” sound instead. In classical Arabic, “my heart” is “Ya Qalbee,” but in Levantine Arabic, it is “Ya Albee.”
In Palestine, for example, the traditional qaf sound can replace “g” or “k,” and “k” can be replace by “ch.” This is all determined by geographical differences.

There are so many differences between Maghrebi Arabic speakers that they have their own names for their language. They refer to her as Derja, Derija, or Darija. This is written as and means “to rise or advance step by step” in Arabic.
The omission of vowel sounds is a distinguishing feature of the dialect family. For example, in Moroccan Arabic, “min ayna anta” (where are you from?) becomes “mnin nta” in MSA.
The above is a brief explanation of dialect differences.
However, in this blog post, I will attempt to create a comparison to demonstrate how the same words and phrases are spoken in various dialects.
ARE ARABIC DIALECTS MUTUALLY INTELLIGIBLE?
Which Arabic dialects are mutually intelligible? Which Arabic dialects are not mutually intelligible? What is the most intelligible Arabic dialect?
In other words, can native Arabic speakers comprehend you if you speak a particular dialect?
It is challenging to discuss a precise degree that would address this inquiry. There are 22 nations in the Arab World. There is what linguists refer to as a dialect continuum among these nations; i.e., dialects that are close to one another are similar, while dialects that are far apart are mutually incomprehensible.Thta’s why it is important to divide Arabic dialects in 6 major types geographically so become easy to comprehend.
Mutually Intelligible VS not Mutually Intelligible:
Moroccan (Maghrebi), Levantine (Shami), Egyptian (Masri), and Gulf Arabic are the four main dialects of Arabic (Khaleeji). The majority of Arabic speakers can understand both Levantine and Egyptian fairly well. The reason Egyptian Arabic may be the easiest to understand is that Egypt has the largest Arabic-speaking film, television, and music industries. Palestinians, Syrians, Lebanese, and Jordanians are among the many people who speak Levantine Arabic. These region also has a sizable TV and music business.
Levantine and Egyptian are, in my opinion, fairly mutually comprehensible languages.
Most Arabic speakers I’ve spoken to find it quite challenging to comprehend those who speak the Maghrebi dialect. Which is spoken in Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco.
The strong French and Berber influences are probably to blame for this. Nonetheless, speakers of Maghrebi typically have no trouble understanding Levantine and Egyptian Arabic. Furthermore, in my experience, dialect closeness is more important for understanding Gulf Arabic.
Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco are the five Arab nations that are arranged from East to West. Currently, Egyptian Arabic is comparable to Libyan Arabic, Tunisian Arabic is comparable to Tunisian, Algerian Arabic is comparable to Algerian, and Moroccan Arabic is comparable to Moroccan. Moroccan and Egyptian dialects, however, are mutually incomprehensible.
Are Moroccan and Egyptian Arabic mutually intelligible? Do Moroccans identify as Arabs? Can Moroccans understand standard Arabic?
Almost everyone can understand someone speaking with an accent, but Moroccans are particularly difficult for other Arabic speakers to comprehend. They also struggle to understand other distinctive dialects like Egyptian and Iraqi.
Darja is the moniker given to people who are from Morocco. Darja vocabulary has a strong French and Tmazight (Berber Language) influence, and it frequently uses Arabic phrases that are not commonly used in the rest of the Arab world.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DIFFERENT ARABIC DIALECTS:
A COMPARISON FAQs:
1. How many different dialects of Arabic are there?
The Arabic language is divided into three dialects: Quranic or Classical, Modern Standard, and Colloquial or Daily. These three versions encompass approximately 25 dialects, some of which are mutually incomprehensible and others that are barely distinguishable.
2. What is the oldest Arabic dialect?
The Arabic language derives from the Safaitic dialect.
The Syro-Arabian desert nomadic tribes used the Safaitic dialect, which is the oldest dialect in old Arabic. After Safaitic and other versions of old Arabic, Classical Arabic emerged.
3. What is the purest Arabic dialect?
Modern Stander Arabic
4. What’s the easiest Arabic dialect?
Egyptian Arabic is arguably the easiest variety of Arabic to learn for all those interested in learning Arabic, particularly English speakers. There are many English words in Egyptian Arabic, and many Arabic loan words have been introduced into English by Egyptians since the British occupation of Egypt.
5. What is the softest Arabic dialect?
Arabic in the Levant
Many Arabic students prefer Levantine because it is the softest of all Arabic dialects. Not to mention, because this language is speakes in four countries, it is likely that many learners who are originally from these countries will want to learn their own dialects.