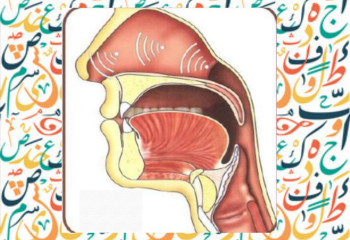
The letter ta ت is the third letter of Arabic alphabets. Here you will learn how to pronounce ta ت and how to write ta ت . You will also learn the different shapes of letter ta ت with examples.
Equivalent of letter ta ت in English
The letter ta ت equivalent in English is letter T and has “t” phonics.
It is unique in it self as it has two dots over it.
It has the same shape as of baa ب letter but difference is that baa ب has one dot under it and it ت has two dost over it.
As in Arabic letters dots n position of dot is very important as it can make big difference. You will learn it more in later posts as you will learn other Arabic letters.
How to pronounce ta ت
How to write letter ta ت
Different shapes of ta ت
| final | middle | starting | isolated |
| ـت | ـتـ | تـ | ت |
Examples of ta ت in isolated shape:
نَبَات (nabat) – Plant
حَيات (hiyat) – Life
َمَمات (mamat) – Death
Examples of ta تـ in starting shape:
تاج (taaj) – Crown
تابل (taabil) – Table
تفاحة (tuffaha) – Apple
Examples of ta ـتـ in middle shape:
ستارة (sitaara) – Curtain
مستقبل (mustaqbal) – Future
حتى (hatta) – Until
Examples of ta ـت in final shape:
كتبت (katabat) – she wrote
حرمت (ḥarramt) – Prohibited
شتات (shataat) – dispersion
Articulation Point of ta ت
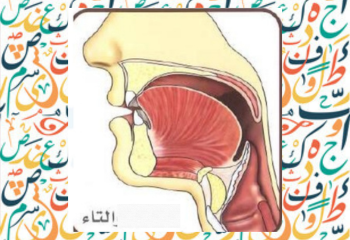
Letter ta ت is pronounce by the tip of tongue and the gum line of the two top incisor meet while the back portion of the tongue is lowered.
Ta ت is a sun letter
The distinction of “sun letters” (حروف الشمس) and “moon letters” (حروف القمر) is fundamental in determining the pronunciation of the definite article “ال” (al) when it precedes certain consonants in Arabic.
When the definite article “ال” is added to a word starting with a sun letter, a seamless assimilation occurs. For example, “الشمس” (ash-shams) means “the sun,” with the “l” sound smoothly blending into the following “sh.”
When the definite article “ال” is applied to words starting with moon letters, the “l” sound remains distinct. For instance, “القمر” (al-qamar) signifies “the moon,” with the “l” sound clearly separate from the following “q.”
So ta “ت” is a sun letter
The letter “ت” (ta) in Arabic is indeed a sun letter. When the definite article “ال” (al) is prefixed to a word beginning with “ت,” assimilation occurs, and the “l” sound of “al” combines with the “t” sound of “ت.”
Here are some examples:
- التّاءبون (at-taiboon) – “those who repent”
- التاج (at-taj) – “the crown”
Characteristics of letter ta ت
The traits of the letters set them apart from other letters that have the same articulation point.
The proper use of the letter characteristics clarifies the letters and explains the different timings of the saakin letters, which is a crucial concept.
It is evident from examining the qualities which letters have strong and weak makeup. This indicates that examining the qualities of the letters and how they are used is a crucial component.
Letters can be categorized according to what sets them apart:
- Contrasting Characteristics in Letters (الصِفَاتُ المُتَضادَة): These letters have different qualities.
- Letters with Distinctive Qualities: These lack diametrically opposed elements.
Characteristics of Arabic Letters with Contrasting Attributes (الصِفَاتُ المُتَضادَة)
Arabic letter ta ت has following Contrasting Attributes :
| LETTERS | 1. Al Hams – الْهَمْسُ / al Jahr – الجَهْرُ | 2. Ash-shidda – الشِّدَّةُ/al baynya – البَينية/ ar Rakhawa – الرَّخَاوَةُ | 3. Al-istiala – الاِسْتِعَلاءُ / al-istifal – الاسْتِفَالُ | 4. Al-itbaq الإِطْبَاق /. Al infitah الإِنْفِتَاح | 5. Al-idhlaq الإِذْلاقُ /. Al ismat(الإِصْمَات |
| ta ت | Al Hams – الْهَمْسُ | Ash-shidda – الشِّدَّةُ | al-istifal – الاسْتِفَالُ | Al infitah الإِنْفِتَاح | Al ismat (الإِصْمَات |
Characteristics of Arabic Letters with Distinctive Attributes (الصِفَات غَيْر المُتَضادَة)
Arabic letter ta ت has following Distinctive Attributes :
| 1. As-Safeer (الصَفِير) | 2. Al-Qalqala (القَلْقَلَة) | 3. Al-leen – اللِّيْن | 4. Al inhiraf – الإِنْحِراف | 5. At-takreer – التَّكْرِير | 6. At tafashee – التَّفَشِي | 7. Al istitala – الإِسْتِطَالَة | 8. Al gunna – غُنّه |
| ————- | ———— | ———— | ———— | ———— | ———— | ———— | ———— |
Complete letters: